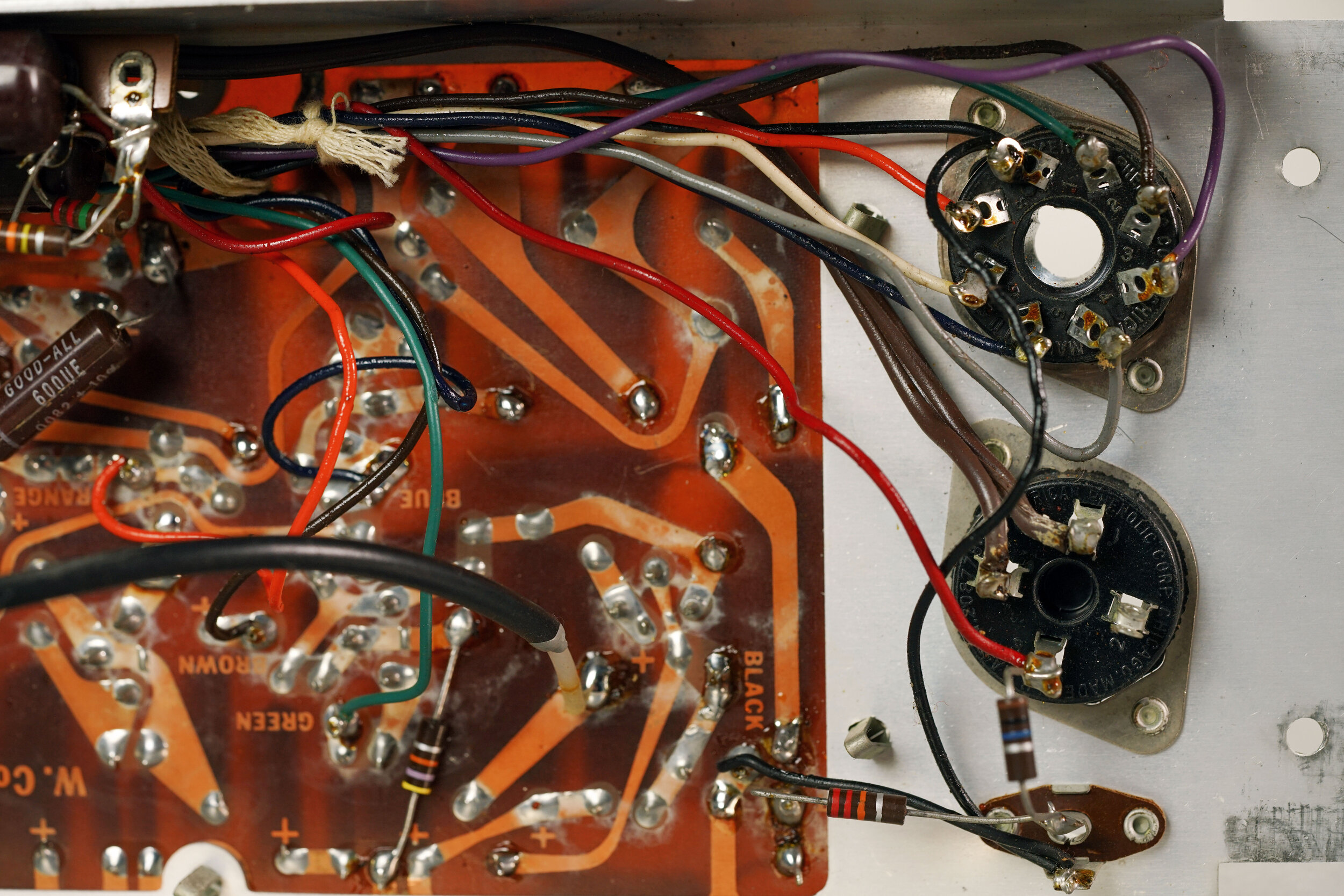
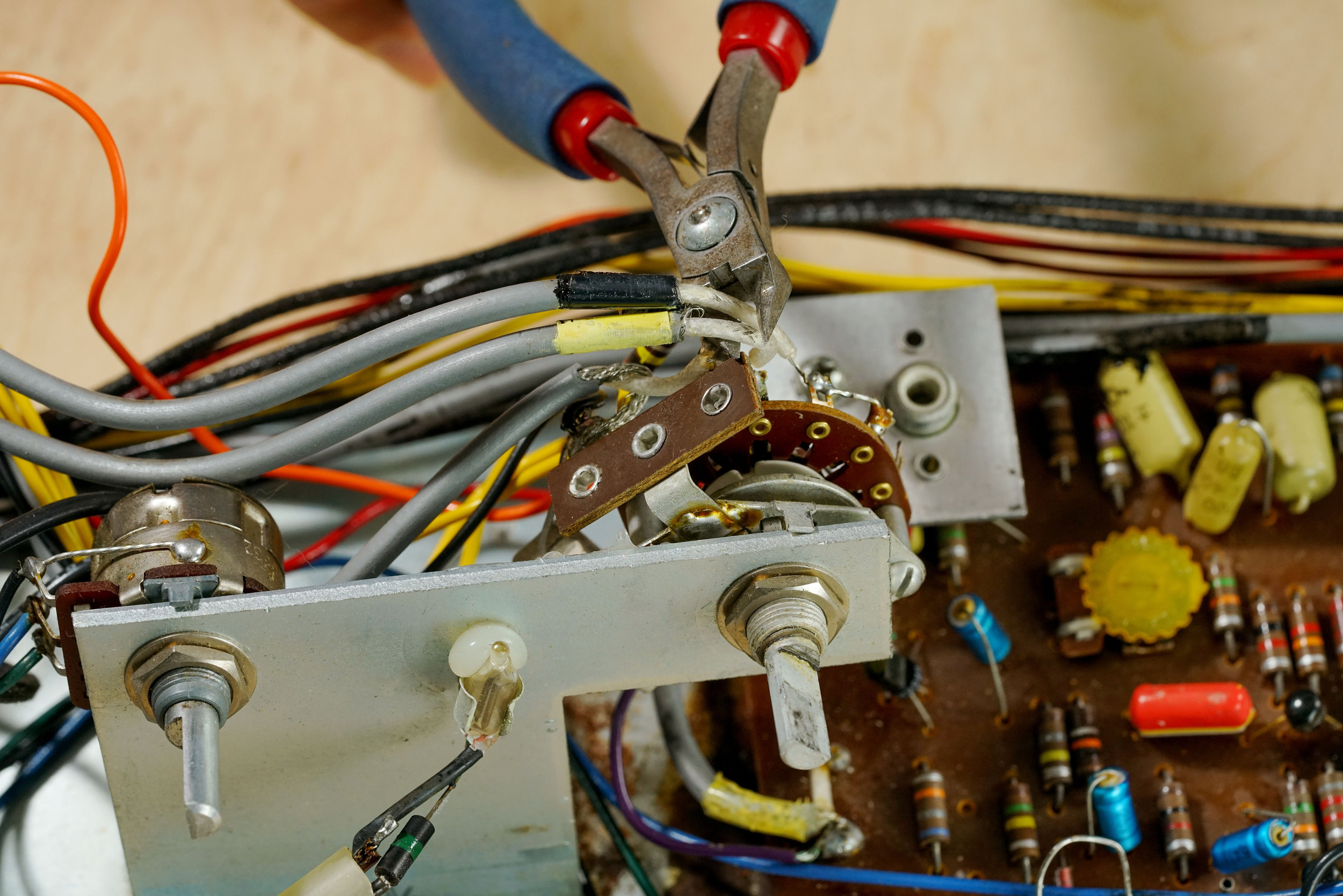
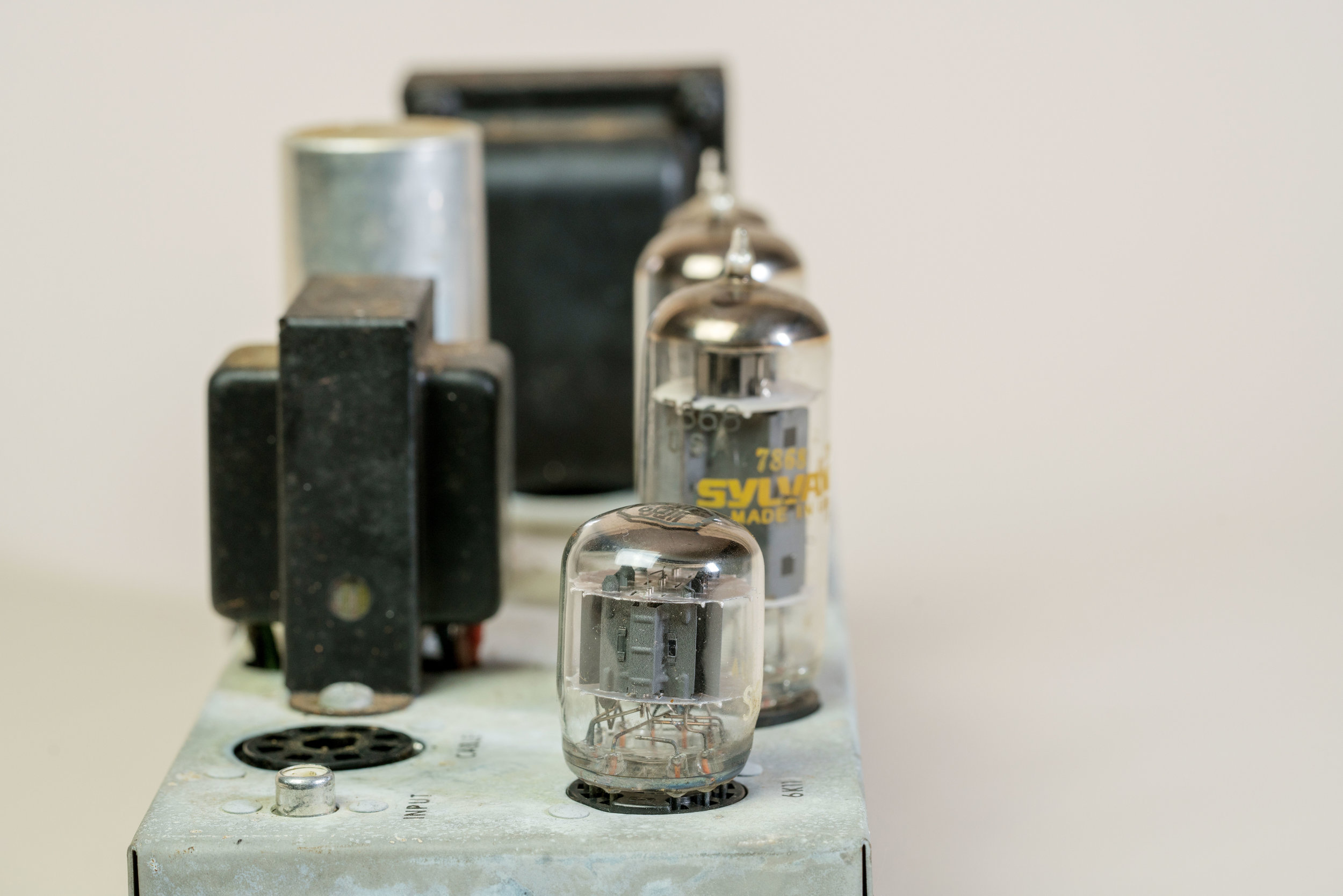Common Tube Amp Malfunctions: My amp makes no sound.
If your amp makes no sound, it is first important to define what you mean by “no sound.” To that end, the first test you should perform is whether you can hear anything coming from the speakers. (This is, of course, after you have eliminated the possibility of trivial problems.)
Listening to what (if anything) comes out of the speakers can help you isolate the problem to specific parts of the circuit. If you hear no sound coming from the speakers — including hum, hiss, reverb crash, input cable pop, or any other incidental, non-musical sounds — the problem could be the speaker itself. But, if you hear non-audio sound coming from the speakers, the problem is likely, although not guaranteed, to be a fault in the preamp section of the circuit.
Common Tube Amp Malfunctions: How to accurately diagnose what is wrong with your vintage amplifier.
If your amplifier isn’t working, the best thing you can do is describe the problem as accurately as possible. If you’re into DIY, using accurate terms will help you google your problem and give you the best search results. If you’re asking a tech or a friend for help, describing your problem with specificity helps them offer more relevant suggestions.
How to Troubleshoot Any Amplifier: Start with trivial problems.
The most efficient way to troubleshoot an amplifier is to investigate common trivial problems first. Complicated problems can have complicated solutions, but trivial problems can often be solved in a matter of minutes. By starting with potential trivial problems, you can cover a lot of ground quickly, without unsoldering a single connection. This reduces wear-and-tear on your amplifier, saves time, and prevents you from replacing components that still have plenty of life left in them.
On Cathode Bypass Capacitors
Cathode bypass capacitors are not absolutely necessary in a circuit. However, their presence or absence in an amplifier affects three things: gain, frequency response, and hum.
If you feel that your amp is lacking in any of these aspects, determining whether the cathodes are bypassed is a good place to start.
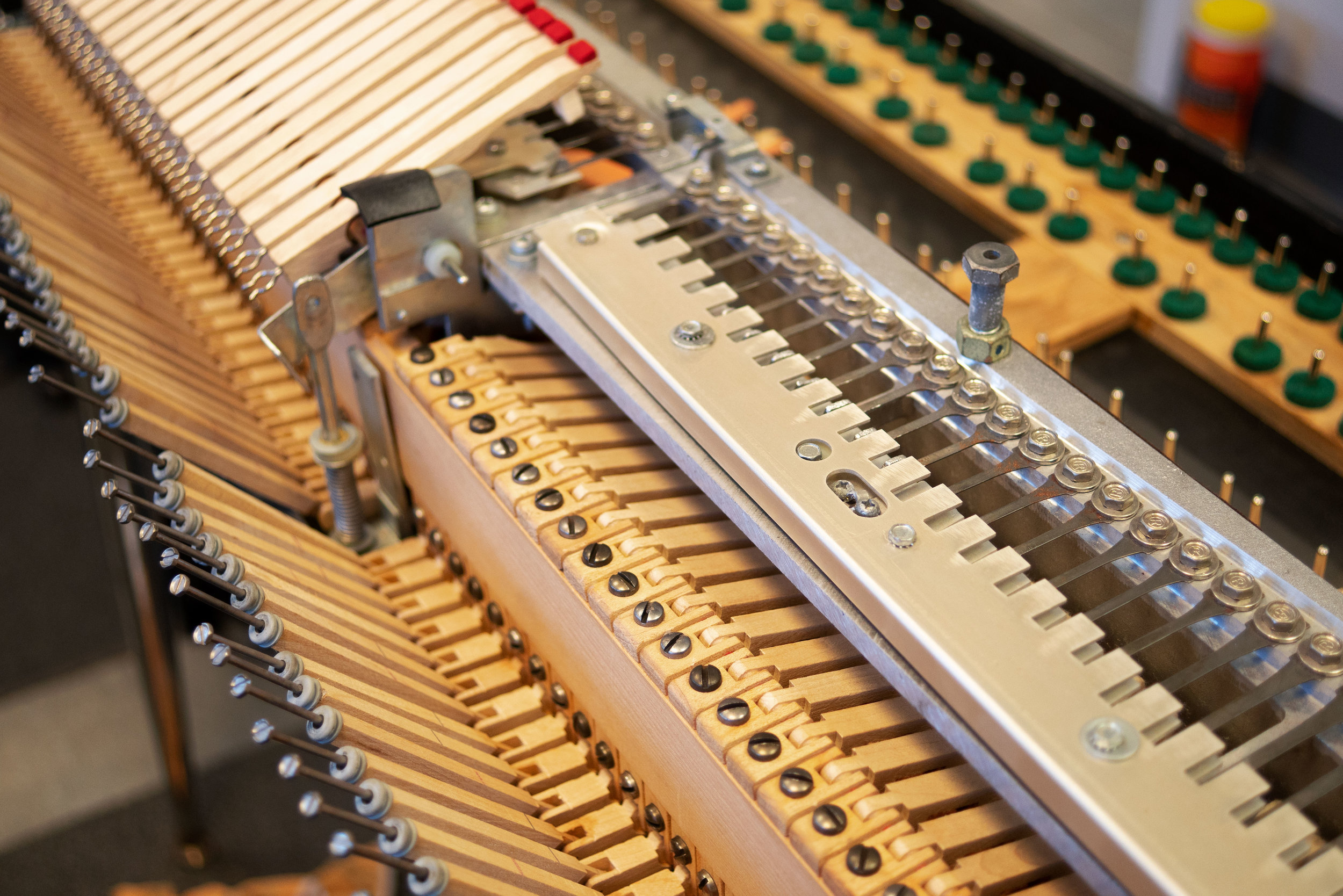
On Modifying a Wurlitzer
Whenever you think about modifying a vintage electronic piano, you should think about two things. Is the mod reversible? And, if not, am I actually improving the keyboard?
A Wurlitzer electronic piano has been around for decades. Clearly, Wurlitzer did something right when they manufactured them, because even after all these years they are still desirable. It is important to avoid performing impulsive mods that will irreversibly change the keyboard. Think it through. Consider whether the mod enhances the function of the keyboard. Consider whether there is a less invasive way to reach the same goal.
What to Look for When Buying a Fender Rhodes Electronic Piano
When we’re thinking about buying a Rhodes, there are a few criteria that we use to judge potential purchases. We’re mostly concerned about how much work the Rhodes needs to become playable - and if you want your Rhodes to be a functional keyboard and not just a moderately inconvenient buffet table, you probably care about the same things we do.
How to Fix Hum in Your Wurlitzer Electronic Piano (Or Other Vintage Amp): Part II
In Part I of our guide on fixing hum, we listed some easy fixes. In Part II, we’ll go into further detail on techniques that require some prior electronics experience to execute. It’s worth checking out Part I first, because it listed some simple, non-invasive things that you should always be tried before diving into the amplifier’s circuitry. For the purposes of this article, we’ll assume that you already tried everything in Part I. This includes:
In Restoration: Removing Duct Tape from the Wurlitzer 140a
This Wurlitzer 140a belonged to a producer for many years, and arrived at our shop in well-used condition. By that, we mean that it was pretty banged up and showed evidence of previous repairs. Also, because multiple latches were missing, the lid didn’t attach very well. At some point, it had obviously once been held in place with duct tape.
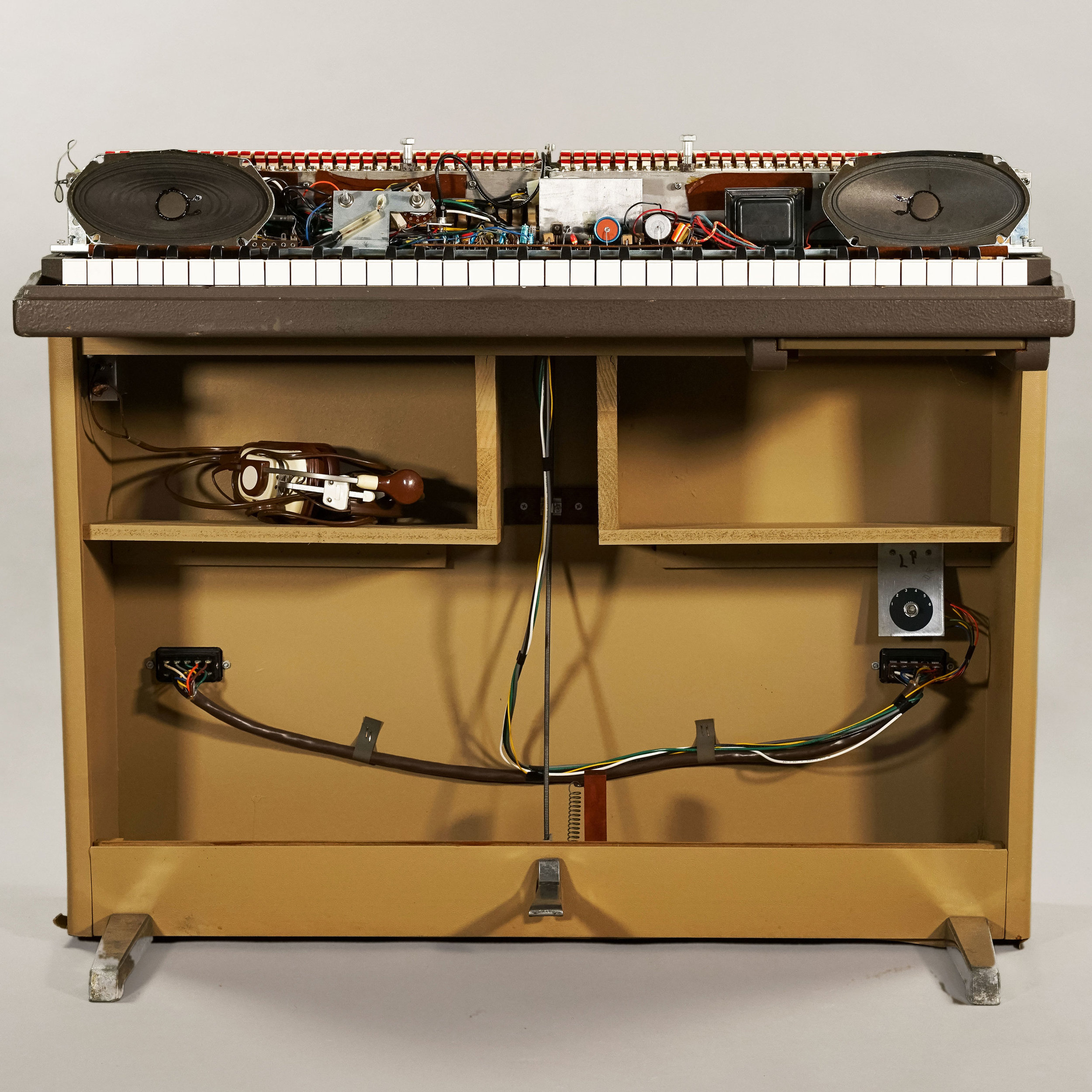
How to Convert a Wurlitzer 206 into a Wurlitzer 200
The Wurlitzer 206 is the student version of the Wurlitzer 200. It is equivalent to the 200 in every day, but it is mounted on a cabinet instead of legs and some features of the amplifier are disabled. However, all of the components that are in a 200 are also present on the circuit board of the 206. Enabling vibrato and the aux output is therefore as simple as adding some wires and a 10k potentiometer. Here is how we do it.
Gibson GA-5 vs Fender 5F1: Circuit Analysis
We’ve written about the history of the Gibson GA-5 before. Basically, the GA-5 was Gibson’s first practice amp offering. Not only was the circuit nearly identical to the Fender Champ, but the GA-5’s cabinet was suspiciously similar as well. Eventually, Gibson adopted a more original exterior design, but the circuit remained pretty much the same. This means that a GA-5 of any vintage is an extremely affordable equivalent to a 5F1 Champ.
How to Convert a Gibson GA-5 to a Fender 5F1 (Or Vice Versa)
We’ve discussed the differences between the GA-5 and 5F1, both historically and in terms of the circuit. Here’s how one circuit could be converted to the other, in list form.
Popping and Crackling Sounds in Wurlitzer Electronic Pianos: Is It the Amp, Or Is It the Reeds?
Popping and crackling sounds are a very common problem in Wurlitzer keyboards. Although they may sound dramatic, they’re most often caused by debris in the reed bar. This is very common and mostly harmless to the amplifier.
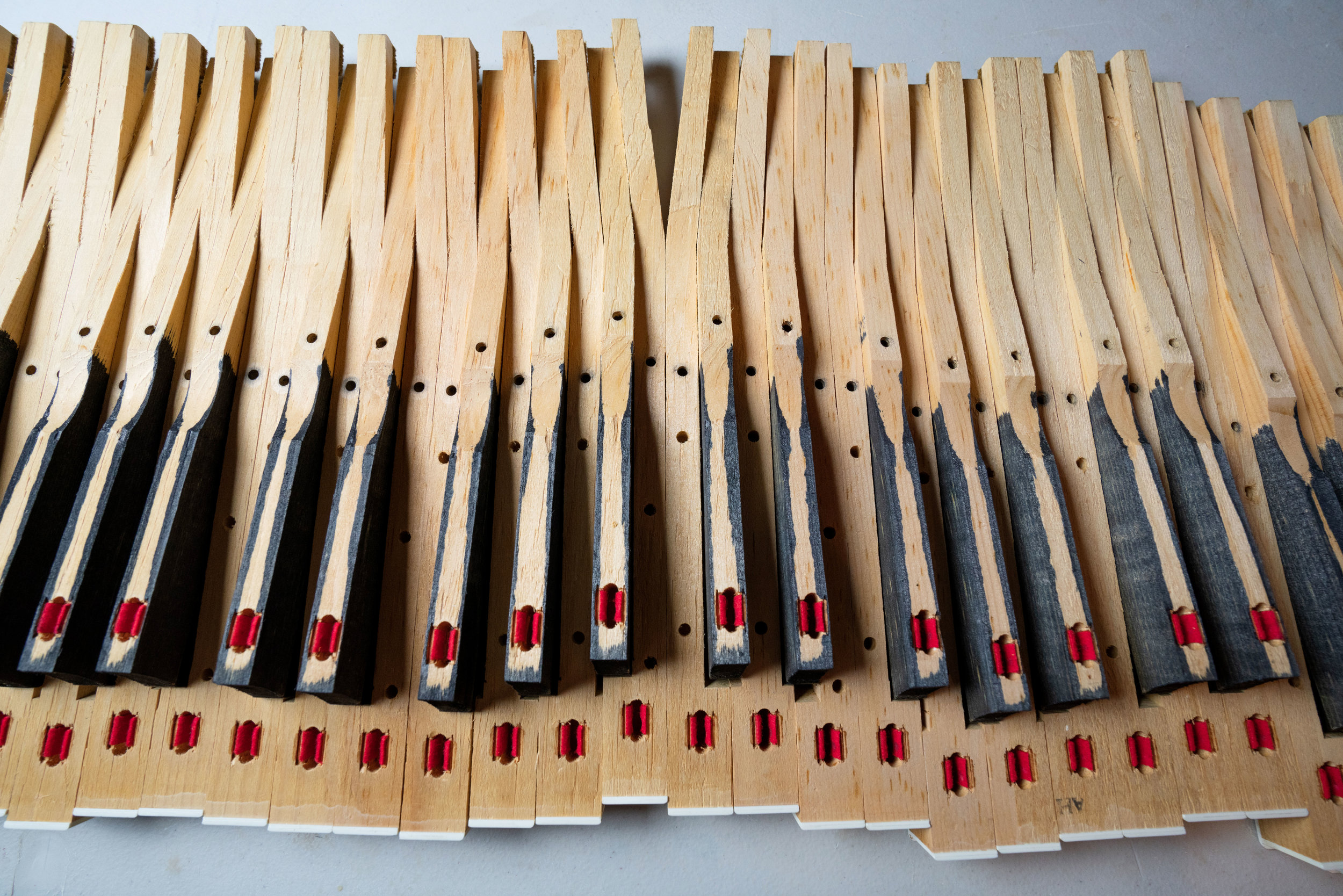
Does My Wurlitzer Need New Key Bushing Felts?
If you flip a Wurlitzer key upside down, you’ll see two holes underneath. These holes line up with the two metal pins in the keybed that guide the key’s vertical travel. They’re called the key bushings, and they’re lined with felt. As the keyboard is played, this felt becomes compressed over time and the keys no longer fit snugly around the key pin. Or, if these felts become damaged, they could prevent the key’s smooth travel and the touch-responsiveness of the keyboard becomes compromised.
Why Are My Wurlitzer's Keys Sticking?
There are many different problems that could make a Wurlitzer’s keys stick. Because sticky keys are so case-specific, there is no cure-all solution. However, here are some ideas as to why your Wurlitzer’s keys are sticking.
A Short Guide to Wurlitzer Electronic Piano Sustain Problems
The most common sustain problem on a Wurlitzer 200a (or earlier) keyboard is too much sustain: the note continues to ring out, even when the pedal is not depressed. This is almost always caused by damper felts that are excessively compressed or otherwise deteriorated. In other cases, the Wurlitzer’s sustain pedal doesn’t do anything when depressed, and the piano never has sustain. This is usually because the pedal is not making the proper interior connection. This guide will help you address both problems.
Techniques for Recording a Wurlitzer Electronic Keyboard
The Wurlitzer electronic keyboard was first commercially released by Wurlitzer in 1955 as a convenient (and potentially silent) tool to practice and study piano. But, almost immediately after its release, the instrument was discovered by professional musical talent such as Ray Charles and found its way to stages and recording studios. Because of the instrument’s unmistakably unique and warm tone and numerous practical advantages, it was a solid choice for recording artists from the very beginning.
Easy Fixes for Malfunctioning Wurlitzers
Some issues involving a vintage Wurlitzer electronic piano are complex to resolve. Others are caused by loose hardware, disconnected wires, or pieces of debris. If you’d like to try some easy fixes before you call a tech, here are some steps that you can take.
Steps to Restoring a Vintage Wurlitzer Keyboard
How do we restore a Wurlitzer electronic piano? Here’s a list of all the issues we commonly address.
Allen & Heath GS-3: Cleaning the Knobs on a Vintage Console
When we received our Allen & Heath GS3, it was caked in dust but otherwise in great working condition. We wanted it to sparkle like the technological marvel it was when it was released in 1994, so we took it apart and gave it a deep clean.
Choose the Right Wurlitzer Model with our Quick Guide to Wurlitzers!
Having trouble deciding which Wurlitzer model is right for you? Take a look at our handy infographic!
This infographic is an at-a-glance guide to the features of common Wurlitzer models. All models of Wurlitzers are excellent instruments, and with the right restoration any one of them can become a functional, professional piece of gear. However, all Wurlitzers were manufactured 40+ years ago, at a time when standards for recording were much different. And, anyway, professional musicians weren’t necessarily the most lucrative target audience: that would be schools, who bought keyboards six at a time. So, some features that would be standard today - such as an aux output - are absent from many models.